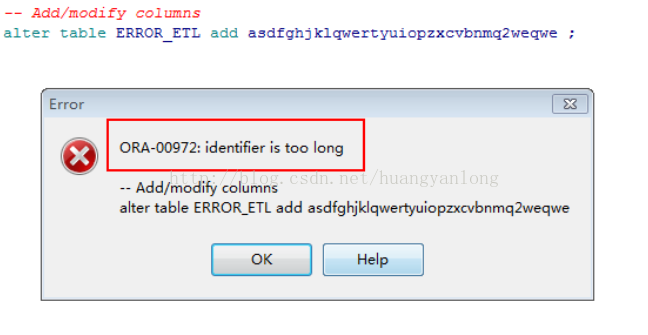
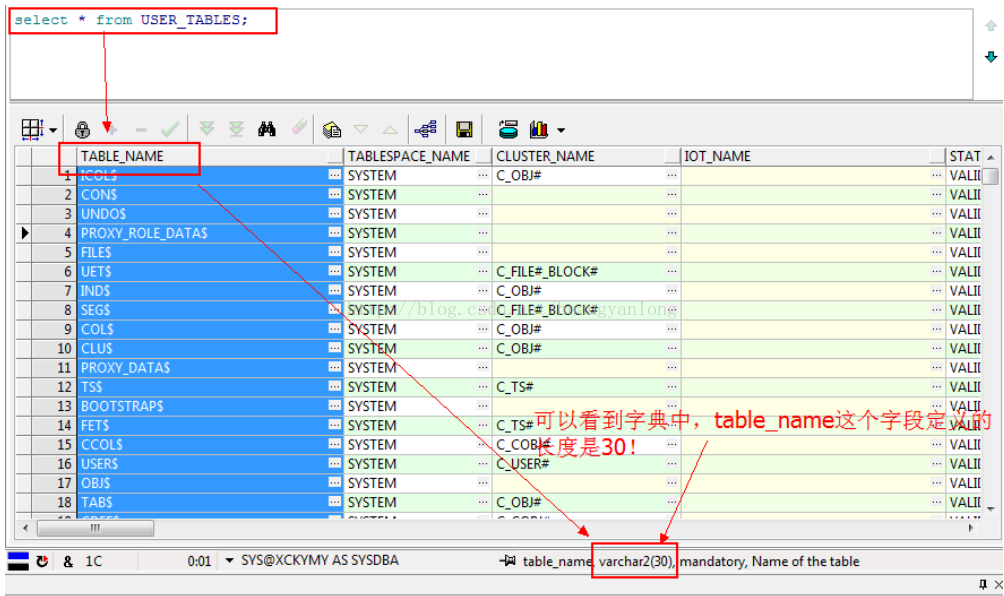
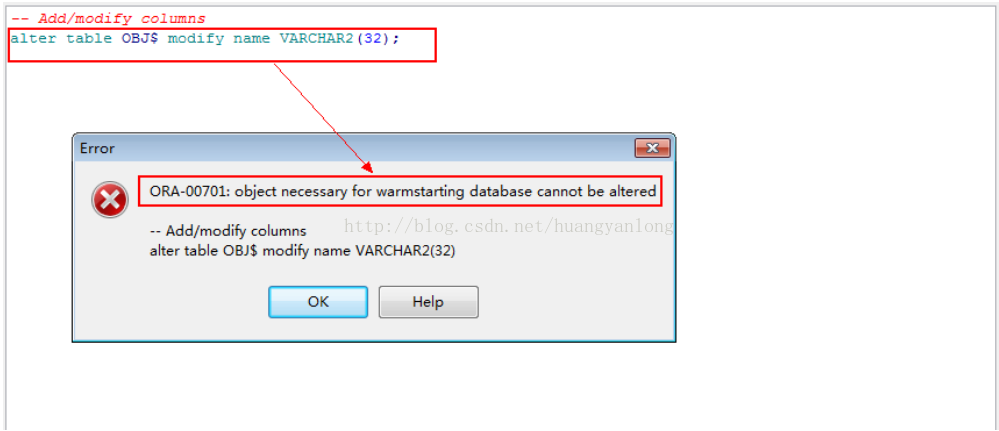
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
| create or replace view user_tables
(table_name, tablespace_name, cluster_name, iot_name, status, pct_free, pct_used, ini_trans, max_trans, initial_extent, next_extent, min_extents, max_extents, pct_increase, freelists, freelist_groups, logging, backed_up, num_rows, blocks, empty_blocks, avg_space, chain_cnt, avg_row_len, avg_space_freelist_blocks, num_freelist_blocks, degree, instances, cache, table_lock, sample_size, last_analyzed, partitioned, iot_type, temporary, secondary, nested, buffer_pool, flash_cache, cell_flash_cache, row_movement, global_stats, user_stats, duration, skip_corrupt, monitoring, cluster_owner, dependencies, compression, compress_for, dropped, read_only, segment_created, result_cache)
as
select o.name,
decode(bitand(t.property,2151678048), 0, ts.name,
decode(t.ts
decode(bitand(t.property, 1024), 0, null, co.name),
decode((bitand(t.property, 512)+bitand(t.flags, 536870912)),
0, null, co.name),
decode(bitand(t.trigflag, 1073741824), 1073741824, 'UNUSABLE', 'VALID'),
decode(bitand(t.property, 32+64), 0, mod(t.pctfree$, 100), 64, 0, null),
decode(bitand(ts.flags, 32), 32, to_number(NULL),
decode(bitand(t.property, 32+64), 0, t.pctused$, 64, 0, null)),
decode(bitand(t.property, 32), 0, t.initrans, null),
decode(bitand(t.property, 32), 0, t.maxtrans, null),
decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.initial_stg * ts.blocksize,
s.iniexts * ts.blocksize),
decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.next_stg * ts.blocksize,
s.extsize * ts.blocksize),
decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.minext_stg, s.minexts),
decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.maxext_stg, s.maxexts),
decode(bitand(ts.flags, 3), 1, to_number(NULL),
decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.pctinc_stg, s.extpct)),
decode(bitand(ts.flags, 32), 32, to_number(NULL),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 2), 2, 1,
decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.frlins_stg, decode(s.lists, 0, 1, s.lists)))),
decode(bitand(ts.flags, 32), 32, to_number(NULL),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 2), 2, 1,
decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.maxins_stg, decode(s.groups, 0, 1, s.groups)))),
decode(bitand(t.property, 32+64), 0,
decode(bitand(t.flags, 32), 0, 'YES', 'NO'), null),
decode(bitand(t.flags,1), 0, 'Y', 1, 'N', '?'),
t.rowcnt,
decode(bitand(t.property, 64), 0, t.blkcnt, null),
decode(bitand(t.property, 64), 0, t.empcnt, null),
decode(bitand(t.property, 64), 0, t.avgspc, null),
t.chncnt, t.avgrln, t.avgspc_flb,
decode(bitand(t.property, 64), 0, t.flbcnt, null),
lpad(decode(t.degree, 32767, 'DEFAULT', nvl(t.degree,1)),10),
lpad(decode(t.instances, 32767, 'DEFAULT', nvl(t.instances,1)),10),
lpad(decode(bitand(t.flags, 8), 8, 'Y', 'N'),5),
decode(bitand(t.flags, 6), 0, 'ENABLED', 'DISABLED'),
t.samplesize, t.analyzetime,
decode(bitand(t.property, 32), 32, 'YES', 'NO'),
decode(bitand(t.property, 64), 64, 'IOT',
decode(bitand(t.property, 512), 512, 'IOT_OVERFLOW',
decode(bitand(t.flags, 536870912), 536870912, 'IOT_MAPPING', null))),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 2), 0, 'N', 2, 'Y', 'N'),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 16), 0, 'N', 16, 'Y', 'N'),
decode(bitand(t.property, 8192), 8192, 'YES',
decode(bitand(t.property, 1), 0, 'NO', 'YES')),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 2), 2, 'DEFAULT',
decode(bitand(decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.bfp_stg, s.cachehint), 3),
1, 'KEEP', 2, 'RECYCLE', 'DEFAULT')),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 2), 2, 'DEFAULT',
decode(bitand(decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.bfp_stg, s.cachehint), 12)/4,
1, 'KEEP', 2, 'NONE', 'DEFAULT')),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 2), 2, 'DEFAULT',
decode(bitand(decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184,
ds.bfp_stg, s.cachehint), 48)/16,
1, 'KEEP', 2, 'NONE', 'DEFAULT')),
decode(bitand(t.flags, 131072), 131072, 'ENABLED', 'DISABLED'),
decode(bitand(t.flags, 512), 0, 'NO', 'YES'),
decode(bitand(t.flags, 256), 0, 'NO', 'YES'),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 2), 0, NULL,
decode(bitand(t.property, 8388608), 8388608,
'SYS$SESSION', 'SYS$TRANSACTION')),
decode(bitand(t.flags, 1024), 1024, 'ENABLED', 'DISABLED'),
decode(bitand(o.flags, 2), 2, 'NO',
decode(bitand(t.property, 2147483648), 2147483648, 'NO',
decode(ksppcv.ksppstvl, 'TRUE', 'YES', 'NO'))),
decode(bitand(t.property, 1024), 0, null, cu.name),
decode(bitand(t.flags, 8388608), 8388608, 'ENABLED', 'DISABLED'),
case when (bitand(t.property, 32) = 32) then
null
when (bitand(t.property, 17179869184) = 17179869184) then
decode(bitand(ds.flags_stg, 4), 4, 'ENABLED', 'DISABLED')
else
decode(bitand(s.spare1, 2048), 2048, 'ENABLED', 'DISABLED')
end,
case when (bitand(t.property, 32) = 32) then
null
when (bitand(t.property, 17179869184) = 17179869184) then
decode(bitand(ds.flags_stg, 4), 4,
case when bitand(ds.cmpflag_stg, 3) = 1 then 'BASIC'
when bitand(ds.cmpflag_stg, 3) = 2 then 'OLTP'
else decode(ds.cmplvl_stg, 1, 'QUERY LOW',
2, 'QUERY HIGH',
3, 'ARCHIVE LOW',
'ARCHIVE HIGH') end,
null)
else
decode(bitand(s.spare1, 2048), 0, null,
case when bitand(s.spare1, 16777216) = 16777216
then 'OLTP'
when bitand(s.spare1, 100663296) = 33554432
then 'QUERY LOW'
when bitand(s.spare1, 100663296) = 67108864
then 'QUERY HIGH'
when bitand(s.spare1, 100663296) = 100663296
then 'ARCHIVE LOW'
when bitand(s.spare1, 134217728) = 134217728
then 'ARCHIVE HIGH'
else 'BASIC' end)
end,
decode(bitand(o.flags, 128), 128, 'YES', 'NO'),
decode(bitand(t.trigflag, 2097152), 2097152, 'YES', 'NO'),
decode(bitand(t.property, 17179869184), 17179869184, 'NO',
decode(bitand(t.property, 32), 32, 'N/A', 'YES')),
decode(bitand(t.property,16492674416640),2199023255552,'FORCE',
4398046511104,'MANUAL','DEFAULT')
from sys.ts$ ts, sys.seg$ s, sys.obj$ co, sys.tab$ t, sys.obj$ o,
sys.deferred_stg$ ds, sys.obj$ cx, sys.user$ cu, x$ksppcv ksppcv,
x$ksppi ksppi
where o.owner
and o.obj
and bitand(t.property, 1) = 0
and bitand(o.flags, 128) = 0
and t.bobj
and t.ts
and t.file
and t.block
and t.ts
and t.obj
and t.dataobj
and cx.owner
and ksppi.indx = ksppcv.indx
and ksppi.ksppinm = '_dml_monitoring_enabled'
;
comment on table USER_TABLES is 'Description of the user''s own relational tables';
comment on column USER_TABLES.TABLE_NAME is 'Name of the table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.TABLESPACE_NAME is 'Name of the tablespace containing the table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.CLUSTER_NAME is 'Name of the cluster, if any, to which the table belongs';
comment on column USER_TABLES.IOT_NAME is 'Name of the index-only table, if any, to which the overflow or mapping table entry belongs';
comment on column USER_TABLES.STATUS is 'Status of the table will be UNUSABLE if a previous DROP TABLE operation failed,
VALID otherwise';
comment on column USER_TABLES.PCT_FREE is 'Minimum percentage of free space in a block';
comment on column USER_TABLES.PCT_USED is 'Minimum percentage of used space in a block';
comment on column USER_TABLES.INI_TRANS is 'Initial number of transactions';
comment on column USER_TABLES.MAX_TRANS is 'Maximum number of transactions';
comment on column USER_TABLES.INITIAL_EXTENT is 'Size of the initial extent in bytes';
comment on column USER_TABLES.NEXT_EXTENT is 'Size of secondary extents in bytes';
comment on column USER_TABLES.MIN_EXTENTS is 'Minimum number of extents allowed in the segment';
comment on column USER_TABLES.MAX_EXTENTS is 'Maximum number of extents allowed in the segment';
comment on column USER_TABLES.PCT_INCREASE is 'Percentage increase in extent size';
comment on column USER_TABLES.FREELISTS is 'Number of process freelists allocated in this segment';
comment on column USER_TABLES.FREELIST_GROUPS is 'Number of freelist groups allocated in this segment';
comment on column USER_TABLES.LOGGING is 'Logging attribute';
comment on column USER_TABLES.BACKED_UP is 'Has table been backed up since last modification?';
comment on column USER_TABLES.NUM_ROWS is 'The number of rows in the table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.BLOCKS is 'The number of used blocks in the table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.EMPTY_BLOCKS is 'The number of empty (never used) blocks in the table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.AVG_SPACE is 'The average available free space in the table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.CHAIN_CNT is 'The number of chained rows in the table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.AVG_ROW_LEN is 'The average row length, including row overhead';
comment on column USER_TABLES.AVG_SPACE_FREELIST_BLOCKS is 'The average freespace of all blocks on a freelist';
comment on column USER_TABLES.NUM_FREELIST_BLOCKS is 'The number of blocks on the freelist';
comment on column USER_TABLES.DEGREE is 'The number of threads per instance for scanning the table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.INSTANCES is 'The number of instances across which the table is to be scanned';
comment on column USER_TABLES.CACHE is 'Whether the table is to be cached in the buffer cache';
comment on column USER_TABLES.TABLE_LOCK is 'Whether table locking is enabled or disabled';
comment on column USER_TABLES.SAMPLE_SIZE is 'The sample size used in analyzing this table';
comment on column USER_TABLES.LAST_ANALYZED is 'The date of the most recent time this table was analyzed';
comment on column USER_TABLES.PARTITIONED is 'Is this table partitioned? YES or NO';
comment on column USER_TABLES.IOT_TYPE is 'If index-only table, then IOT_TYPE is IOT or IOT_OVERFLOW or IOT_MAPPING else NULL';
comment on column USER_TABLES.TEMPORARY is 'Can the current session only see data that it place in this object itself?';
comment on column USER_TABLES.SECONDARY is 'Is this table object created as part of icreate for domain indexes?';
comment on column USER_TABLES.NESTED is 'Is the table a nested table?';
comment on column USER_TABLES.BUFFER_POOL is 'The default buffer pool to be used for table blocks';
comment on column USER_TABLES.FLASH_CACHE is 'The default flash cache hint to be used for table blocks';
comment on column USER_TABLES.CELL_FLASH_CACHE is 'The default cell flash cache hint to be used for table blocks';
comment on column USER_TABLES.ROW_MOVEMENT is 'Whether partitioned row movement is enabled or disabled';
comment on column USER_TABLES.GLOBAL_STATS is 'Are the statistics calculated without merging underlying partitions?';
comment on column USER_TABLES.USER_STATS is 'Were the statistics entered directly by the user?';
comment on column USER_TABLES.DURATION is 'If temporary table, then duration is sys$session or sys$transaction else NULL';
comment on column USER_TABLES.SKIP_CORRUPT is 'Whether skip corrupt blocks is enabled or disabled';
comment on column USER_TABLES.MONITORING is 'Should we keep track of the amount of modification?';
comment on column USER_TABLES.CLUSTER_OWNER is 'Owner of the cluster, if any, to which the table belongs';
comment on column USER_TABLES.DEPENDENCIES is 'Should we keep track of row level dependencies?';
comment on column USER_TABLES.COMPRESSION is 'Whether table compression is enabled or not';
comment on column USER_TABLES.COMPRESS_FOR is 'Compress what kind of operations';
comment on column USER_TABLES.DROPPED is 'Whether table is dropped and is in Recycle Bin';
comment on column USER_TABLES.READ_ONLY is 'Whether table is read only or not';
comment on column USER_TABLES.SEGMENT_CREATED is 'Whether the table segment is created or not';
comment on column USER_TABLES.RESULT_CACHE is 'The result cache mode annotation for the table';
|